Formulation optimization of multicomponent aqueous coground mixtures of Meloxicam for dissolution enhancement
Abstract
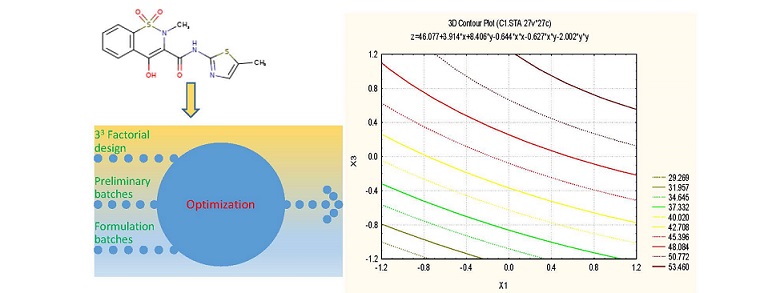
In present work, the role of various formulation excipients for dissolution enhancement of a BCS Class II drug, meloxicam was studied by formulating multicomponent aqueous coground mixtures using lactose, microcrystalline cellulose and three solubilizers; polyethylene glycol 400, propylene glycol and polyvinyl pyrrolidone. A 33 full factorial design was employed using solubilizers’ concentrations as independent variables whereas angle of repose and in vitro drug dissolution as dependent variables in order to optimize the amounts of solubilizers. The results revealed more than fivefold increase in drug dissolution in some experimental batches compared to that of pure drug powder. Full and reduced models were evolved for the dependent variables and the reduced models were further validated using extra design check points. The studies suggested that the incorporation of optimized amounts of solubilizers could be successfully employed for achieving desired flow properties and enhanced drug dissolution of poorly water soluble meloxicam. The method emerged as a simple, cost-effective, and organic solvent-free green approach toward formulation development of meloxicam and may also be applied to other limited water-soluble drugs.



