AC conductivity and dielectric investigations on pure and potassium doped (Na2O+3TiO2) ceramics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.mns.2025.V12.1200Keywords:
Ceramics, AC conductivity, Dielectric constant, TiO2, Q-factor, Conductive materialsAbstract
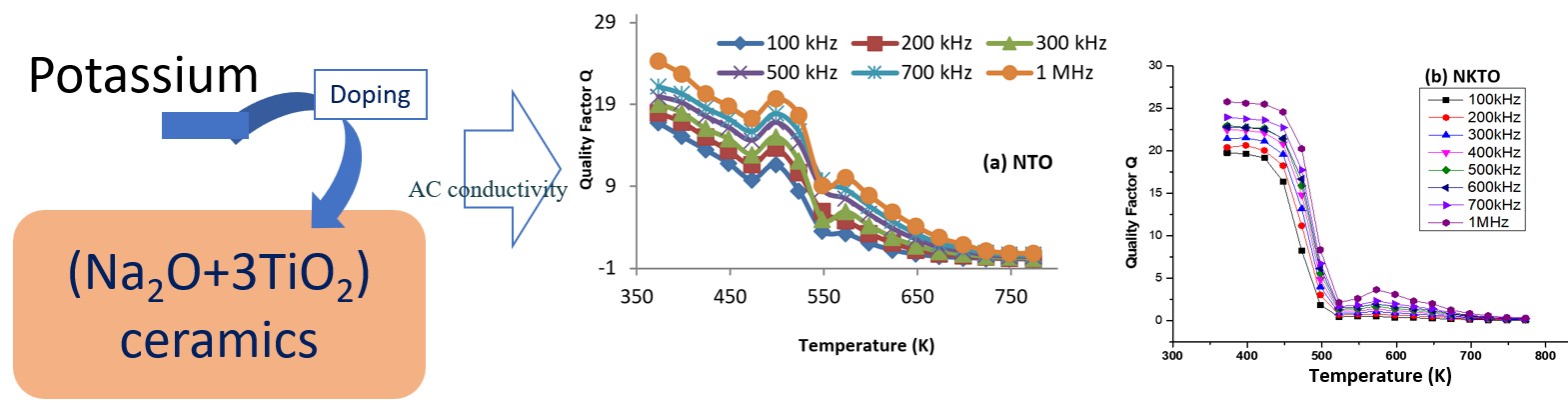
Sodium oxide and titanium dioxide ceramic (Na2O+3TiO2) was synthesized by the conventional ceramic technique. Potassium doped version of the ceramic was synthesized by mixing sodium oxide and potassium oxide in the stoichiometric ratio (Na1.98O+K0.02O). Thin cylindrical pellets of the samples were characterized by ac electrical conductivity and dielectric measurements. In this paper, we report the frequency and temperature dependence of the electrical conductivity, dielectric constant and the dielectric losses of these ceramics. The results suggest the presence of possible ferroelectric phase transitions at higher temperature. These investigations also provide vital information about nature of the dielectric losses and Q-factors in these ceramics under applied ac field. Ionic and /or electronic conductions are observed in different temperature ranges. The mechanism lying behind the electrical conduction in these materials is also investigated and explained.





