Mechanistic investigation of Quercetin in the management of complications of Diabetes mellitus by Network Pharmacology
Keywords:
Network pharmacology, Quercetin, Diabetes, Hyperglycemia, Protein-Protein InteractionAbstract
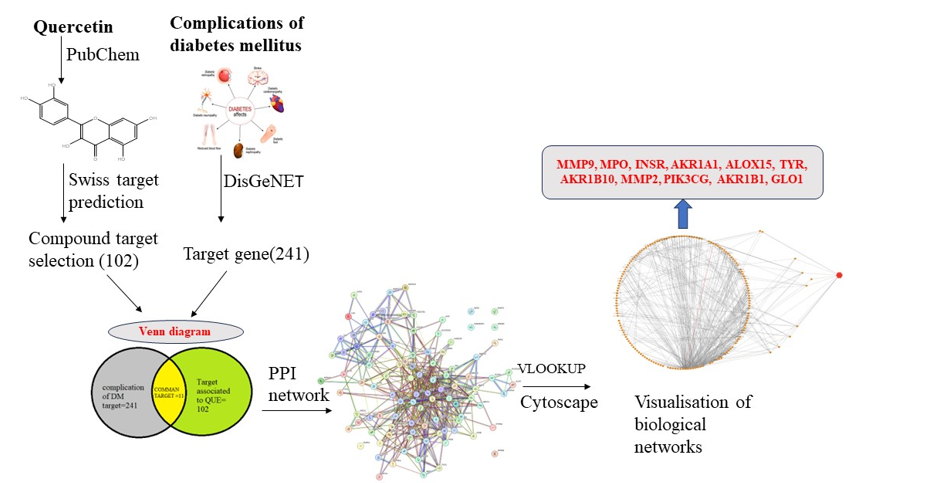
Quercetin is a health supplement that can assist in managing complications associated with diabetes. This study employed modern methods such as network pharmacology to investigate the mechanism by which quercetin protects against diabetes-related complications. Various comprehensive databases (Pubchem, Swiss target prediction database, SEA database, String database, Disgenet database) were used to obtain quercetin-associated targets and genes related to diabetes mellitus complications. The obtained targets were analyzed and intersected to obtain mapping targets, and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed to identify candidate targets. These targets were then ranked to obtain key targets. The major pathways for quercetin were obtained from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway were MMP9, MPO, INSR, AKR1A1, ALOX15, TYR, AKR1B10, MMP2, PIK3CG, AKR1B1, GLO1 found to be responsible for management and control of diabetes-associated complications.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2024.684
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Sonia Kamboj, Minky Mukhija, Jyoti Monga, Riya Singla, Jasmine Chaudhary

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



